Cougar Age and Sex Identification Guide
By Cougar Specialist Rich Beausoleil, Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife
Age Classification Chart
With normal body condition, most mountain lions should fall within the parameters of this identification chart.
| Weight (pounds) |
Male Age | Male Class |
Female Age | Female Class |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2mo | Kitten | 2mo | Kitten | Spots very evident |
| 20 | 4mo | Kitten | 4mo | Kitten | Spots evident |
| 30 | 5mo | Kitten | 5mo | Kitten | Spots somewhat evident (hip area) |
| 40 | 6mo | Kitten | 6mo | Kitten | No spots. Double canine1(perm is shorter) |
| 50 | 7mo | Kitten | 8mo | Kitten | Double canine1 (~equal length) |
| 60 | 8mo | Kitten | 10mo | Kitten | Perm canine ¾ erupted |
| 70 | 9mo | Kitten | 12mo | Sub-adult | No yellowing on teeth |
| 80 | 10mo | Kitten | 14mo | Sub-adult | No yellowing on teeth |
| 90 | 11mo | Kitten | 24mo | Sub-adult | No yellowing on teeth |
| 100 | 12mo | Sub-adult | Over 24mo | Adult | No yellowing on teeth |
| 110 | 14mo | Sub-adult | Over 24mo | Adult | No yellowing on teeth |
| 120 | 18mo | Sub-adult | Over 24mo | Adult | Light yellowing on teeth |
| 1302 | 24mo | Adult | unlikely | Light yellowing on teeth | |
| 1402 | Over 24mo | Adult | unlikely | More yellowing on teeth (at 4 yrs. yellow is prominent) |
1 Double canine references to the deciduous canine and the permanent adult canine being present for a short time.
2 Only males get above 115 pounds.
Determining Sex

Here are two photos of a cougar’s backside. The photo on the left is an 8-month old female and the right side is an adult male. Notice the black spot of hair on the adult male (it surrounds the penis sheath), only males have this black spot (kittens are harder to differentiate but follow a similar pattern).
Also, notice that the anus on both sexes is directly under the tail but how the male has the distinct spacing (3-4 inches) between the anus and the scrotum. The female parts are much closer together.
Determining Age from Teeth
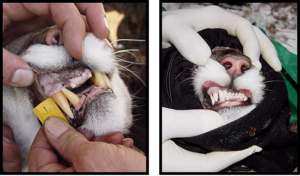
LEFT: An adult female. Notice the yellowing of the teeth and the worn incisors. Also notice the length of her canine compared to the kitten on the right. This cougar’s canines are still fairly sharp; they get duller with age.
RIGHT: A 7-month old cougar showing a double canine of equal length; the rear canine is about to fall out.
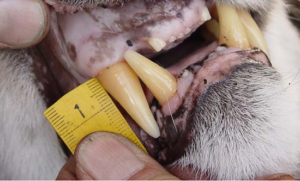
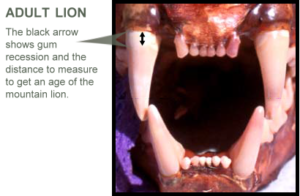
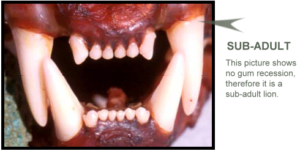
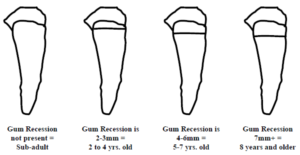
The two examples of gum recession above will help you classify a cougar’s age. The first is an adult and the second is a subadult. Notice the gum recession on the adult: from the gum line the tooth is straight before it begins to taper. The sub-adult tooth is tapered throughout (there is no recession until about 1½ years).
Gum Recession Chart
VIEW PRINTABLE VERSION OF THIS PAGE
courtesy of the Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife



 Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter Send Email
Send Email


